The Superhighway project has been controversial from the day it was first announced publicly for many reasons. First, it was routed without regard to the negative impacts it would have on the Cross River National Park (CRNP) and a number of community forests in its path. The path chosen initially for the 260 kilometres Superhighway was carved out in a manner reminiscent of how Africa was partitioned at the Berlin Conference of 1884 – probably over tea and coffee, or as men hunted for game, and for territories. The path showed a disregard for the unique biodiversity of the region and was equally mindless of the climate impact that would ensue from the massive deforestation that the project was bound to cause. There was also no clarity about how the CRSG would ensure that this is not a white elephant project that would only promote the harvesting of timber from the forest and leave a scarred environment and impoverished communities in its wake.
The 23 conditions attached to the approval of the Superhighway project underscore the fact that development must be relevant to its context and must be in the interest of the people and the environment.
The superhighway as initially proposed met stiff resistance because it appeared to have been poorly thought out and directly threatened over 180 communities, water sources, endemic plant and animal species and lacked clarity about what goods would be conveyed from the proposed “deep” sea port at Esighi to Katsina Ala. It also refused to acknowledge that there is an existing highway that is crying out for refurbishing and would very much serve the purpose of linking the end points of the proposed superhighway. What is the allure for this project? Could it be the label “super” attached to it or are there yet to be revealed intentions?
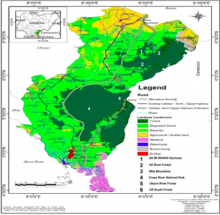
Four Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) submissions down the line, it is now hoped that all stakeholders have learned valuable lessons in project inception and implementation. It should indeed be a sobering and humbling moment with nothing to celebrate for the proponents of the highway that has foisted unnecessary controversy over the supply of a rather basic infrastructure. The 260 km Superhighway has now elongated to 275.344 Km due to the need to avoid the Cross River National Park as well as community forests including the one at Ekuri.
One of the most vexatious impacts of the proposed highway at a point was the revocation of ownership of lands stretching a whopping 10 km on either side of the highway. 10 km on either side of the proposed highway! This was an extremely and ridiculously colonial idea treating the territory literally as a no man’s land. This idea was thrown in the trash bin by the CRSG after receiving much condemnation locally and internationally. We are pleased to see that the Federal Ministry of Environment is insisting that the CRSG should gazette the nullification of that revocation and restrict itself to 70m only as the permissible right of way. This will protect the communities that faced imminent displacement by that attempt at incredible and obnoxious land grab. We also note that one of the conditions is that those that have suffered harm from the project should be compensated. That is the way it should be. The task now is for all stakeholders to monitor and ensure that there is strict compliance with this condition.
The 23 conditions that the Federal Ministry of Environment requires CRSG to fulfil before they would receive the certificate of approval of the EIA necessitates careful study by all stakeholders. It should be carefully and critically examined by communities through which the highway would pass. They also provide civil society and other stakeholders with a template for the detailed monitoring of the overall highway project. Having a conditional EIA approval should be a call on the CRSG to return to the drawing board and get herself ready for the Herculean task of delivering a 275.344km highway that could have been avoided if only she had considered fixing the existing dilapidated Calabar Ogoja highway.
The insistence of the Federal Ministry of Environment that the right thing must be done will eventually help the CRSG to deliver a project that is sensitive to the needs of the people, is not too disruptive of the ecosystems and that will eventually do more good than harm. That is the whole essence of the EIA process. The process has never been political and the resistance by the communities and civil society has been strictly in line with the law.
The conditions require that the Cross River National Park must not be violated by the highway. It also requires that the highway must not tamper with the Ekuri Forest and others. It requires that those whose properties have been tampered with or may be destroyed by the project must be compensated. The gazetting of the cancellation of the revocation order on the 10km stretch on either side of the highway before the project proceeds will ensure that no one’s land is grabbed by stealth. The condition states that the CRSG must “gazette the reversal of revocation order on the acquisition of 10km on either side to the 70km span of the road corridor as well as the gazetting of the boundary of Cross River National Park within two weeks (2) of receipt of this letter.”
Lessons
The conditional EIA approval is a win for everyone – the Federal and State governments as well as the forest communities and the planet as a whole. With the new routing of the Superhighway, there will be less deforestation and thus lessened climate impacts.
The lesson of the conditional approval of the EIA for the superhighway is that it took four attempts at EIA submission before the proponents of this project could come up with something close to passable. Stakeholders note that the CRSG took many decisions without adequate consultations with communities and other stakeholders. Communities were treated with disdain by aristocratic public officers who preferred monologues to dialogues. At a recent Community Dialogue at Akpabuyo, the community people all said they just woke up one day to see bulldozers destroying their crops, land and properties. In other words, they were not consulted. And they were not compensated. One of the conditions given before the EIA would be fully approved is that this anomaly must be corrected. This is a stiff rebuke for a behaviour that should be avoided in future.
We are also pleased to note that CRSG is to ensure that the updated maps in the new EIA must show that the “re-routed road corridor takes cognizance of the boundary of Cross River National Park and Ekuri Community Forest as well as conform to international best practices on setbacks for highways in critical ecosystems such as the proposed corridor.”
The conditional approval is also a stern rebuke for EIA consultants who believe that the exercise is perfunctory and that they can produce a cut-and-paste document with scant relevance to specific project locations. The entire process speaks volumes about the professionalism and quality of service being provided by officers who are saddled with the duties of watching out for the public good. This is where a huge gulf appears between those at the Federal Ministry of Environment and those at the ministry in the Cross River State. The superhighway saga provides a good opportunity for honing of needed skills, engagement with communities and other stakeholders and rebuilding the Cross River brand as a State that benefits from and is deeply appreciative of her cultural and ecological heritage, and acknowledges the intrinsic value of Nature and her gifts. It must also be kept in mind that projects of the size of the proposed highway have present and intergenerational implications. Even if we assume that we don’t owe ourselves an obligation to do the right thing, we cannot avoid a debt that we owe the future.
—- The conditions from the Federal Ministry of Environment-—-
ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT (EIA) APPROVAL FOR THE PROPOSED 275.344KM, CALABAR-IKOM-KATSINA ALA SUPER HIGHWAY PROJECT BY CROSSRIVER STATE GOVERNMENT
Following the successful conclusion of the evaluation of the 4th version of the EIA report, I am directed to convey the Ministry’s EIA Approval for the project subject to the following conditions:
- The EIA approval shall cover only the construction of a 275km long by 70m width Super Highway of 6 lanes including setbacks and other associated infrastructres such as eco-friendly bridges, culverts, drainages from Calabar to Katsina-Ala junction in Cross River State.
- Cross River State Government (CRSG) shall ensure that the construction of the entire road project and associated infrastructures conform to standard engineering codes and International best practices.
- CRSG shall ensure that the diverse management plans, which include Environmental Management Plan (EMP); Biodiversity Action Plan (BAP); Resettlement Action Plan (RAP); Livelihood Restoration Plan (LRP); Greenhouse Gas Management Plan (GHGMP); Public Consultation Plan (PCP); Waste Management Plan (WMP); Traffic Management Plan (TMP) as well as Labour and Human Resources Plan (LHRP) put in place for the road project are strictly adhered to as required throughout the project lifecycle.
- CRSG shall engage a group of accredited Consultants to effectively manage the diverse management plans for the proposed road project.
- CRSG shall ensure the realignment of the 275.344km road corridor from the boundary of the Cross River National Park is in line with the National Park Service (NPS) Act CAP LFN 2016.
- CRSG shall ensure the re-routed road corridor is clearly depicted on a map in the updated EIA report taking cognizance of the boundary of Cross River National Park and Ekuri Community Forest as well as conform to international best practices on setbacks for highways in critical ecosystems such as the proposed corridor.
- CRSG shall gazette the reversal of revocation order on the acquisition of 10km on either side to the 70km span of the road corridor as well as the gazetting of the boundary of Cross River National Park within two weeks (2) of receipt of this letter.
- CRSG shall ensure that the initial land clearing of the road corridor that was carried out without due inventory of the third party properties/farmlands is revisited to adequately compensate the project affected persons (PAPS) in line with National and International standards of practice on resettlement and restoration plans. This shall be done prior to project commencement.
- CRSG shall identify all proximate communities to the road corridor within the established area of influence as well as the project affected persons (PAPS) and ensure that every community/PAP is regularly consulted with throughout the project lifespan.
- The environmental offsetting should be one of the guiding principles for the proposed road construction as the proposed project area of influence is noted for endemic, threatened and endangered flora and fauna. There shall be development and funding of Biodiversity offset by CRSG.
- CRSG shall ensure that all relevant non-governmental organizations both local and international are consulted with regularly during the project lifespan to ensure among others biodiversity protection and project sustainability.
- CSRG shall ensure that the highly technical eco-friendly bridges to be constructed at strategic points/biodiversity hotspots/critical ecosystem on the road corridor are intensively monitored by specialized accredited consultants.
- CSRG shall ensure that the borrow pits proposed for the road project are provided with coordinates for ease of location, site identification number, reclaimed and converted to alternative environmental-friendly uses in line with regulatory standards as well as International best practices.
- CRSG shall ensure that the proposed road setbacks from third party structures, farmlands, critical ecosystem and green areas confirm to Engineering code of practice/regulatory standards as well as International best practices.
- CRSG shall ensure that cautionary signs are appropriately placed at strategic points along the road corridor during implementation and throughout the lifecycle especially for wildlife crossing.
- CSRG shall ensure proper drainage termination for the flow route of run-off/storm water to protect the road corridor from erosion, ensure that the road embankment is constructed in a way that allows free-flow of surface water run-off, that any existing access road to neighbouring villages and settlements are not blocked, create appropriate buffer zones to prevent damage to unique ecosystems as well as enhance forest cover
- CSRG shall put in place appropriate road furniture and safety standards in line with International best practices.
- CRSG shall ensure that the proposed project protect the hydrology of wetlands, streams and channels through restoration of natural drainage pattern and reduce disruption of of ecological processes by providing wildlife corridor.
- CSRG shall provide adequate personal protective equipment for workers, ensure that every worker on the project is adequately trained on Health; Safety and Environment procedures for Highway and provide sanitary facilities and mobile clinic during project construction
- CSRG shall ensure that the maintenance and management of the road corridor is in line with International best practices.
- There shall be Impact Mitigation Monitoring (IMM), Post Impact Assessment (PIA), Environmental Audits and Compliance Monitoring on the project by the Federal Ministry of Environment in collaboration with other relevant regulatory agencies.
- CSRG shall put in place a robust contingency plan for the proposed road project.
- CSRG shall update 4thversion of the EIA report to also include the following:-
- To exclude flora and fauna that are non-existent in the proposed project area of influence as per the attached;
- A comprehensive list of the actual affected communities along the proposed road corridor;
- List of borrow pits with coordinates and site identity for the proposed road project;
- Map clearly showing the preferred road corridor with coordinates as well as major crossings along the entire stretch;
- The EIA report should consider indirect long term impacts of hunting and habitat loss on Cross River National Park proximity to the Super Highway with improved access to the forest.
- The updated 4th version of the EIA report shall be submitted to the Ministry within two (2) weeks of the receipt of the letter.
The Environmental Impact Statement (EIS) and certificate shall be issued for the project in due course.
Further:
The following comments on the fourth (4th) version of the EIA report should be addressed in the updated report.
- The Bunbundi bat (Chalinolobus egeria) has not been recorded from Cross River and the pitch shrew (Crocidura picea) has only ever been recorded from Cameroon.
- The long footed shrew (Crocidura crenata) has not been recorded from Nigeria
- Eisentraut’s mouse shrew (Myosorex eisentrauti) is only found on the island of Bioko.
- The forest chameleon (Chamaeleo camurunensis)- assumed to be Trioseros camerunensis is restricted to Cameroon.
- The Cameroon worm lizard (Cynisca shaeferi) has not been recorded from Nigeria.
- The worm lizard (Cynisca gansi) has only ever been recorded from Okoloma village near PortHarcourt.
- Schneider’s banana frog (Afrixalus Schneider) has only ever been recorded from Cameroon.
- Dizangue reed frog (Hyperrolius bopeleti) is known only from Cameroon
- Werner’s river frog (Phrynobatrachus werneri) has only been recorded in Nigeria from the Obudu Plateau.
- Many of the species listed in Table 6.1 such as the Indian Malimba, Sclater’s guenon and the Anambra waxbill are not present in Cross River State, though known from Nigeria.
- Appendix A2 is clearly not the work of PGM Nigeria Limited and has merely been copied from elsewhere. This is unacceptable. The list contains many species not known from Cross River such as the Niger Delta red colobus monkey (Procolobus epieni); others such as the roloway monkey (Cercopithecus roloway) are not found in Nigeria and some are not even known from Africa such as the American bullfrog (Lithobates catesbaeianus).
- Table 4.56 there is no hedgehog (Erinaceus or Atelerix) found in the rainforests of Cross River State, likely confused with brush-tailed porcupine.
- Table 4.60 lists threatened mammal species, but Cercopithecus erythrogaster is not found in Cross River and Cercopithecus roloway is not found in Nigeria.